Close

where heat is applied.
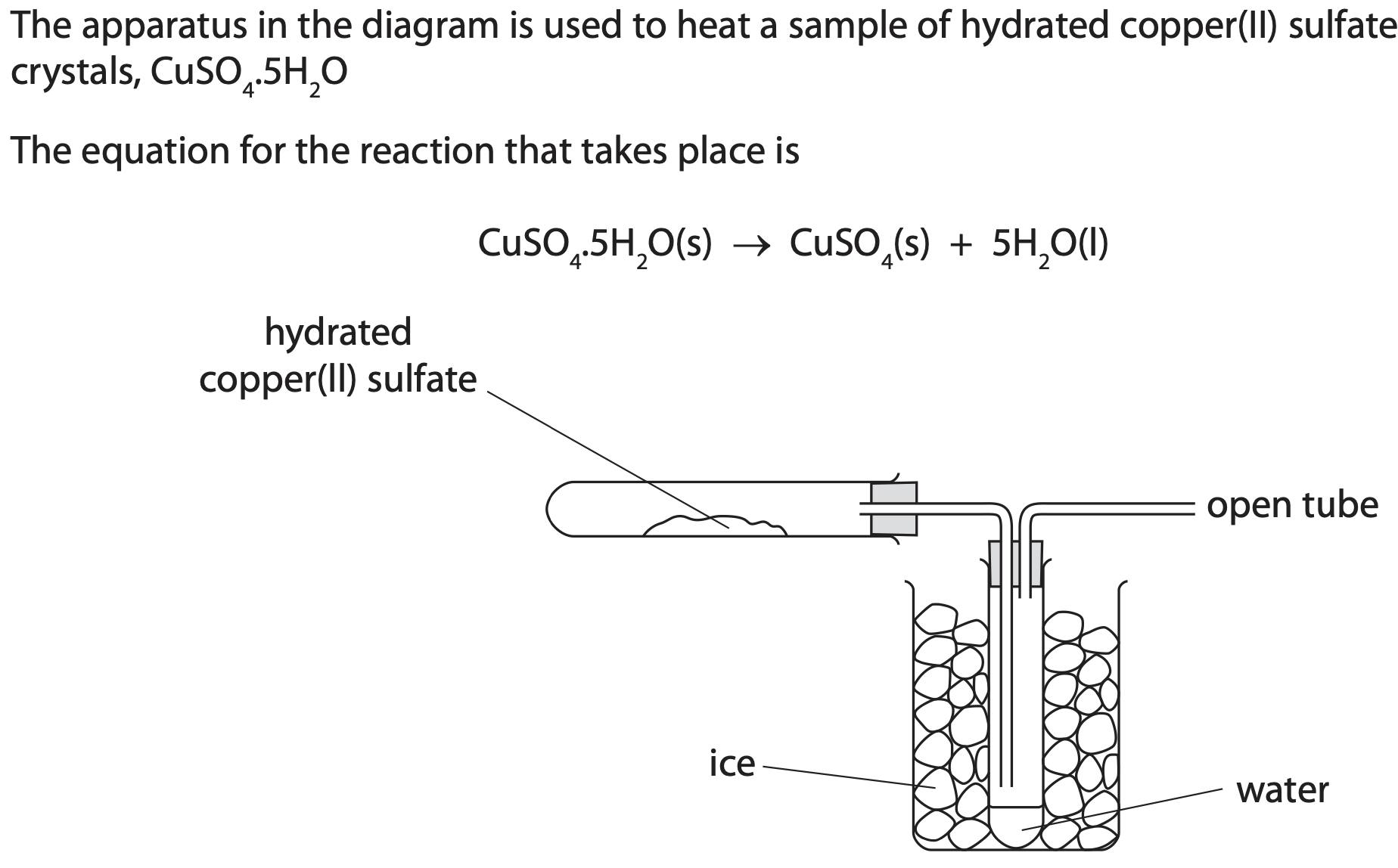
What is the purpose of the ice?

(3)

The name of the salt formed in the student’s experiment is
zinc sulfate
zinc sulfide
zinc sulfite
zinc sulfur
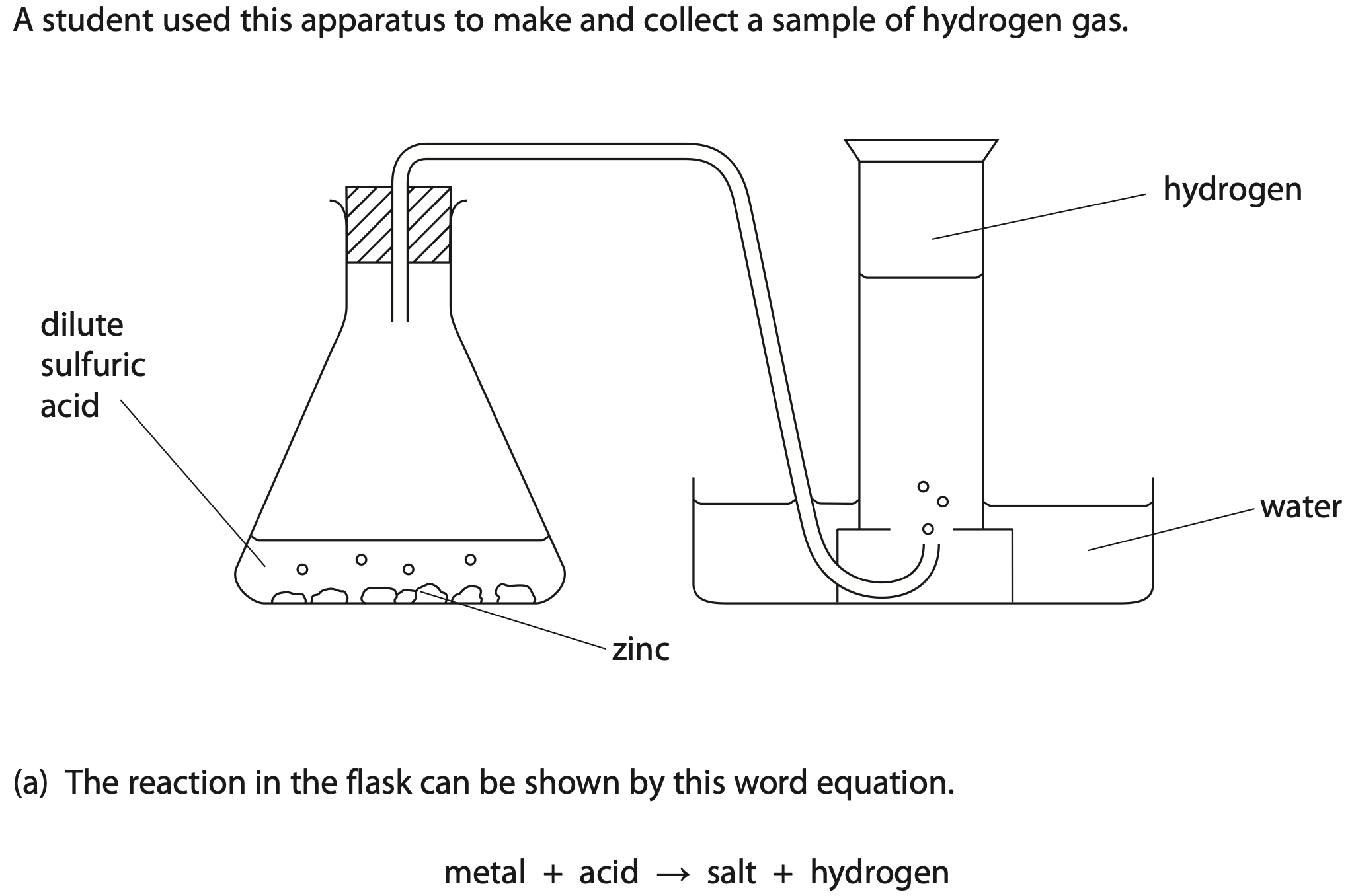
The student could have used two other metals in this experiment to make hydrogen.
copper
iron
magnesium
potassium
silver

Describe a test to show that the gas collected is hydrogen.

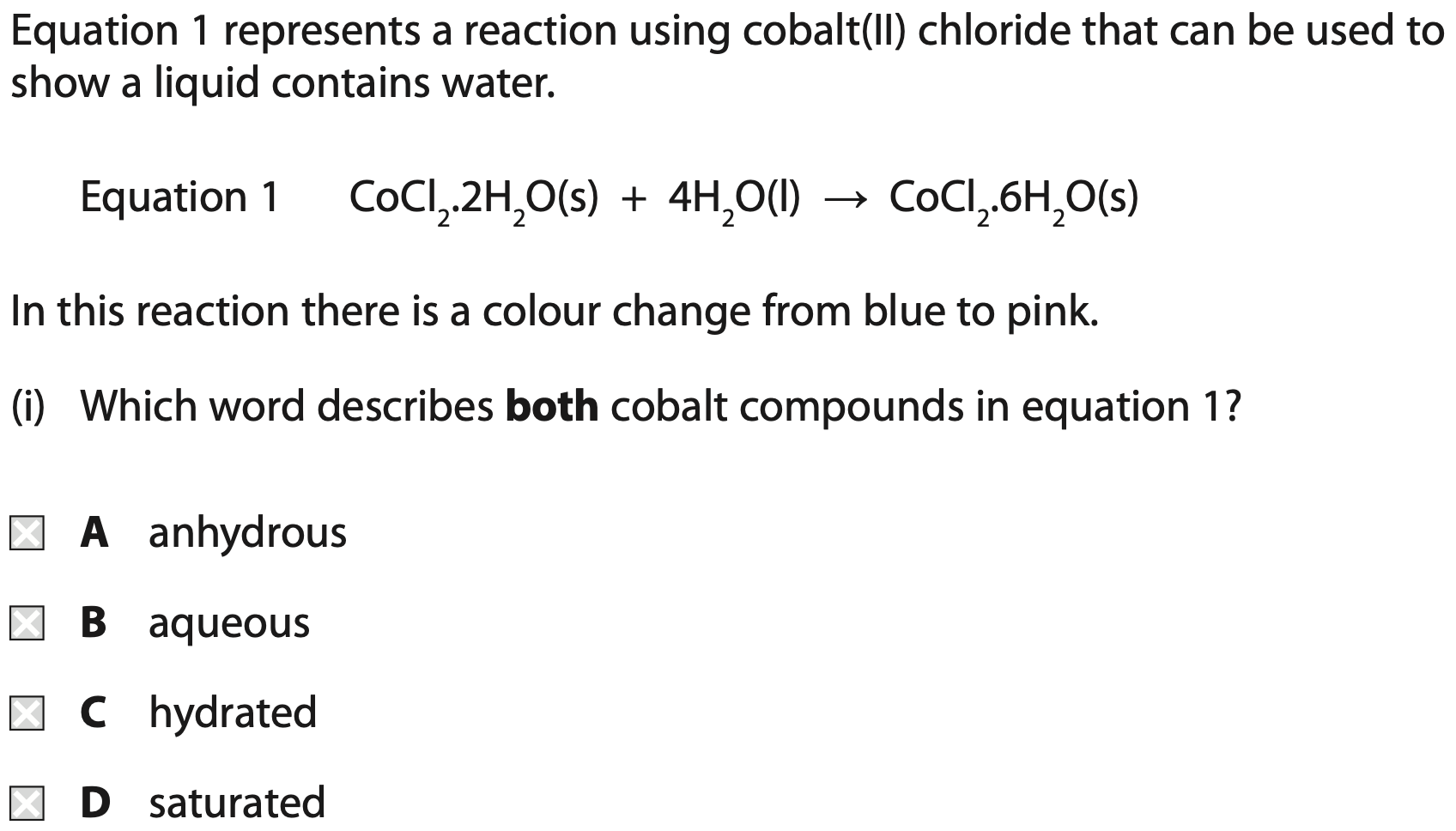
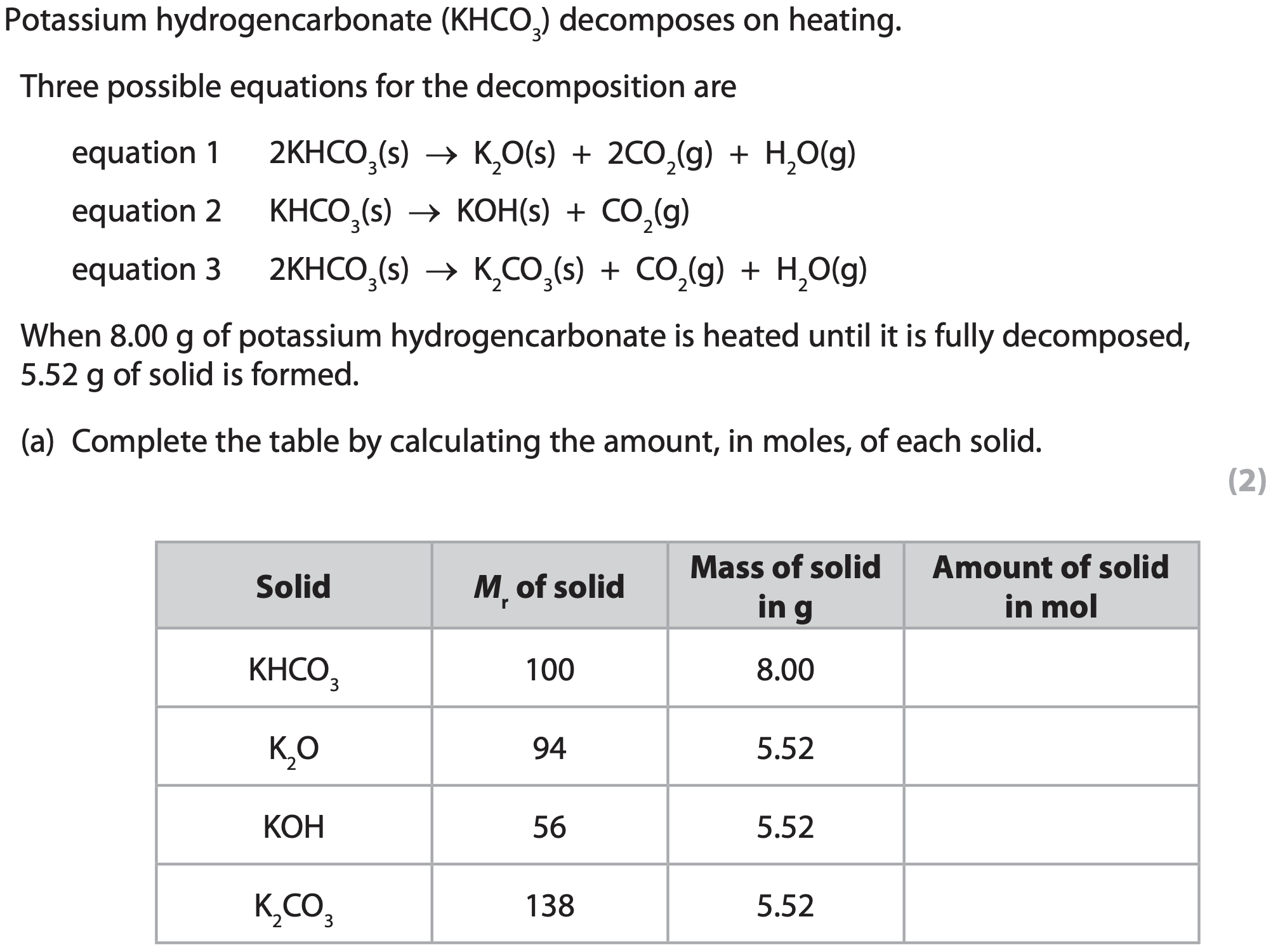
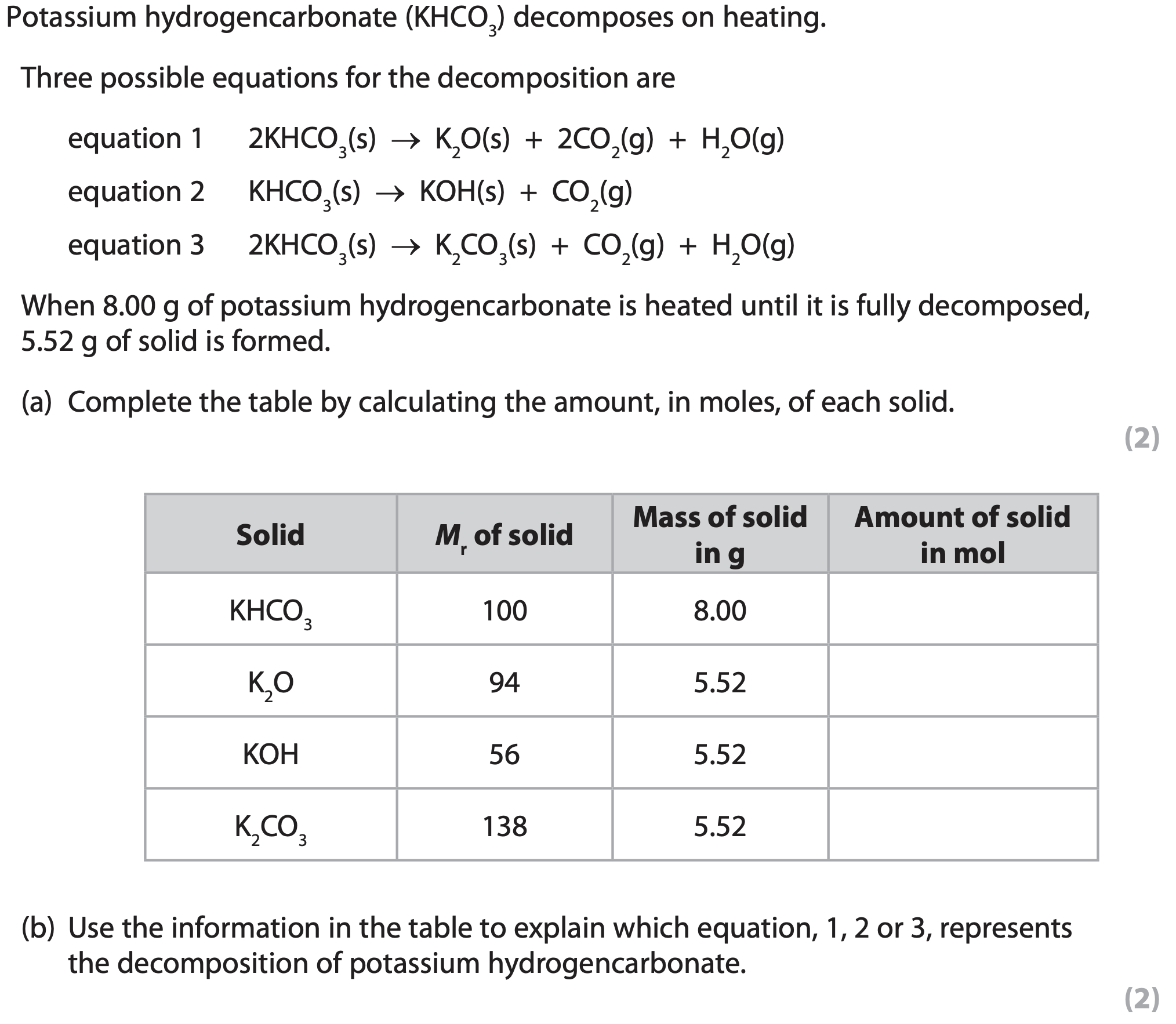
When the product in equation 1 is gently heated, another reaction occurs.
Equation 2 represents this reaction.
What do equations 1 and 2 suggest about the reactions?
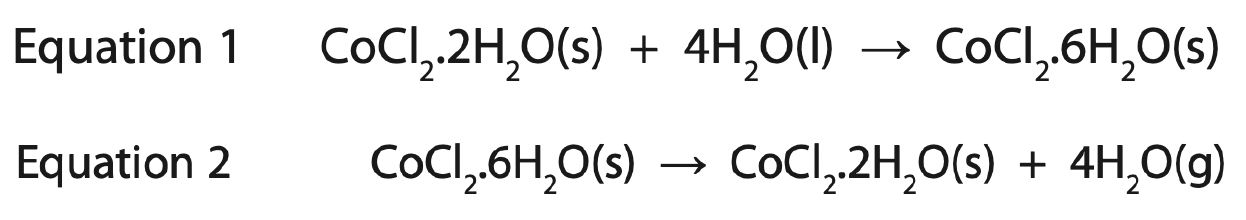
Give the name of this piece of apparatus.
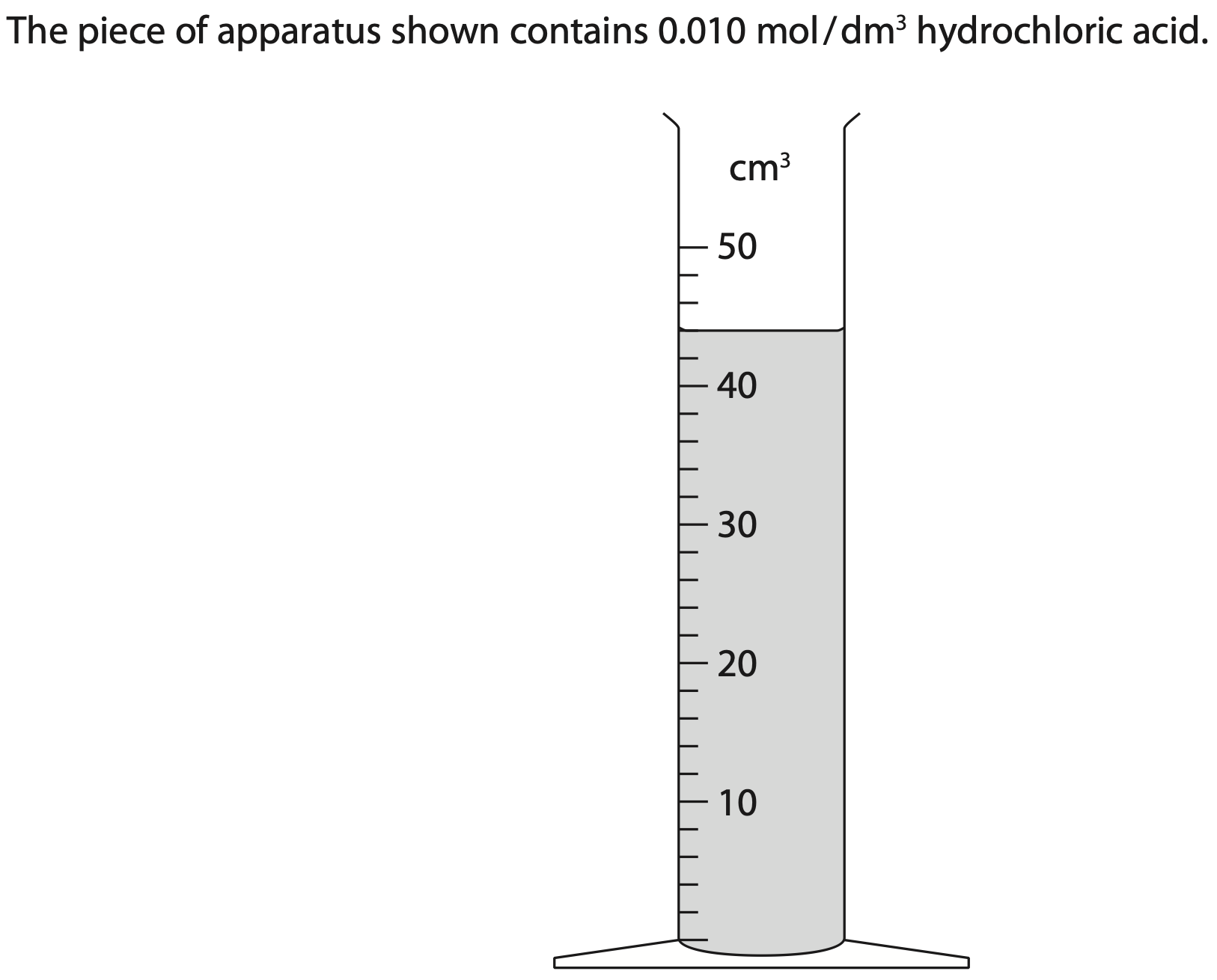
What volume of hydrochloric acid is in the apparatus? (2)

Use the volume of hydrochloric acid in the apparatus to calculate the amount, in moles, of hydrochloric acid in the apparatus.


What effect would this change have on the rate at which the hydrogen is given off?

What effect would this change have on the volume of hydrogen produced?

Look at question 5 on the paper, it's worth 8 marks
In 1774, the scientist Joseph Priestley produced oxygen by heating mercury (II) oxide, (HgO). When heated, mercury (II) oxide breaks down into its elements.
Write a chemical equation for the breakdown of mercury (II) oxide into its elements.
In 1774, the scientist Joseph Priestley produced oxygen by heating mercury (II) oxide, (HgO). When heated, mercury (II) oxide breaks down into its elements.
What name is given to this type of reaction?
Give the name of the apparatus that contains the hydrogen peroxide solution.
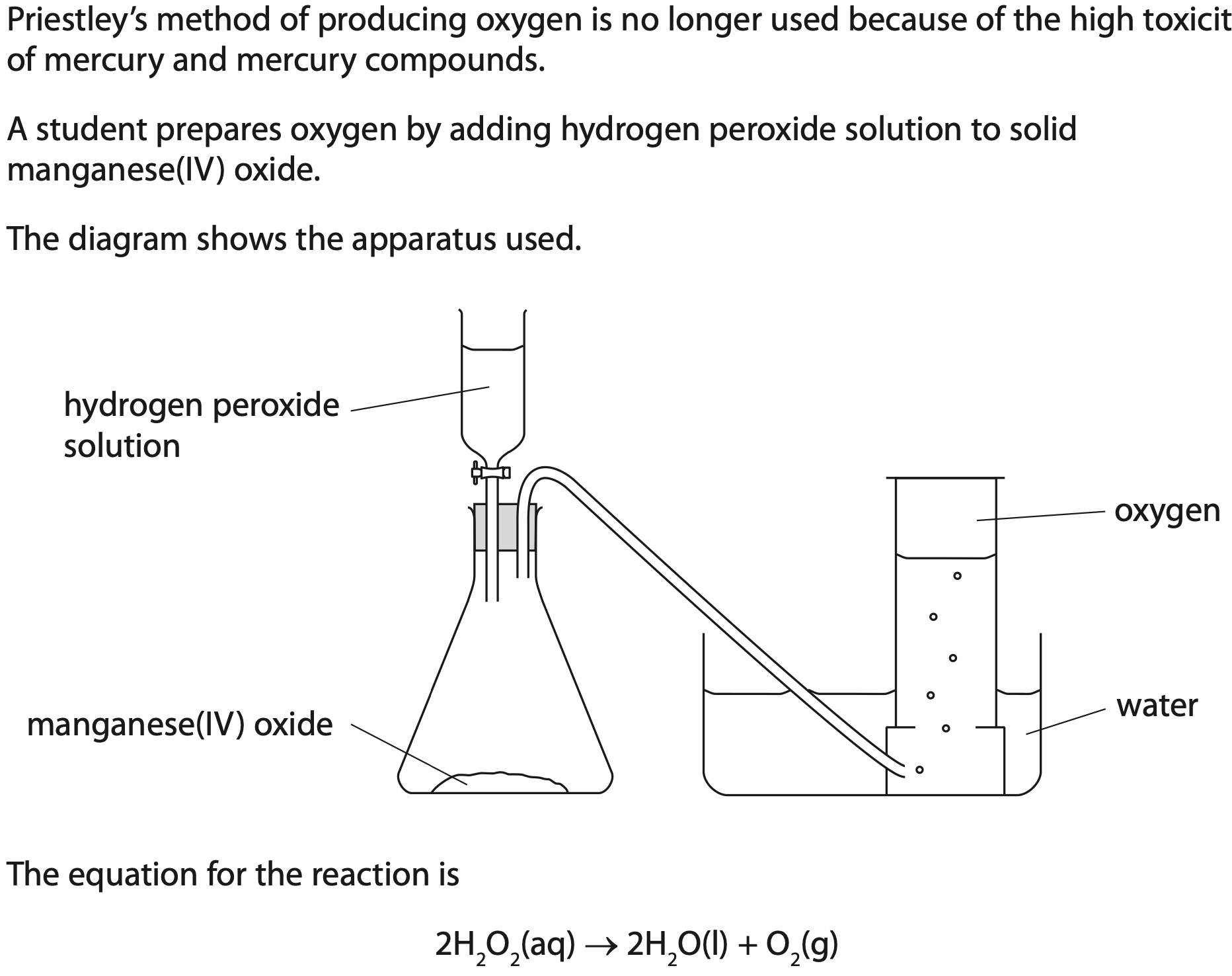
Suggest how the first sample of gas collected may be different from the samples collected later.

A catalyst increases the rate of decomposition of the hydrogen peroxide.
Describe a method you could use to show that the manganese(IV) oxide is acting as a catalyst in this reaction.

Write a chemical equation for the reaction that takes place when sulfur dioxide dissolves in water.

Universal indicator is added to the solution formed in (d)(i). Explain the effect that the solution has on the universal indicator.


 Hide known cards
Hide known cards