Fichas sobre Dargan Muscle Physiology Lectures, creado por sophiakostich el 05/05/2013.
Pineado a
79
1
0
Sin etiquetas
|
|
Creado por sophiakostich
hace más de 11 años
|
|
Cerrar
|
|
Creado por sophiakostich
hace más de 11 años
|
|

Are smooth muscle cells smaller or larger than skeletal muscle cells?
True or false: similarly to skeletal muscle, smooth muscle cells can only hypertrophy - they cannot divide.
Name 3 places you might find smooth muscle.
What are three of the functions of smooth muscle in the body?
True or false: unlike skeletal muscle smooth muscle cells only have one nucleus.
Where does innervation for skeletal muscle come from?
True or false: similarly to skeletal muscle smooth muscle only responds to excitatory stimuli.
How are neurotransmitters passed to smooth muscle due to the lack of post synaptic membrane?
What is the difference in spread of excitation in single-unit smooth muscle cells and multi-unit smooth muscle cells?
Where does the majority of the calcium come from during an AP in smooth muscle?
What is the purpose of latch state of smooth muscle cross bridges?
Between what values does tetanic fusion occur?
What are the two factors that have a variable effect on TFF?
What are the four levels of muscle contraction?
What does fused tetanus result from?
What method can be used to measure motor unit potentials?
In EMG what does the size of the peak relate to?
What increases on an EMG when the strength of contraction in a subject increases?
What is the result of acute denervation?
What are fibrilation potentials?
When does atrophy of muscles occur?
Where does regeneration occur in the neurone?
What is sprouting (of neurones)?
What are the resulting problems of upper motor neurone lesions?
What is myasthenia gravis?
What happens in dystrophin?
What is a twitch a response to and how long do they tend to last?
What is the delay called between an action potential reaching a muscle and the start of contraction.
What is the function of a myogram?
Is a muscle twitch slow or fast compared to an action potential?
Define temporal summation.
Describe how tetanic contraction occurs.
What is physiological classification of muscle fibres dependent on?
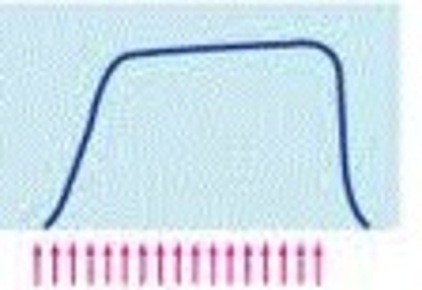
Define contraction time. How can we determine contraction time?
If the frequency is 50 Hz what does this mean for the number of AP per second?
What are the three types of muscle fibres?
Give an example of isometric contraction.
Is the rate of ATP splitting and usage higher in fast twitch or slow twitch fibres?
What is the average speed of contraction in slow twitch fibres?
True or false: all muscle fibres of the same type are supplied by several motor units.
When bench pressing weights what contraction is used: isotonic or isometric?
Do postural muscles or muscles involving fine movements have more motor units?
What would be the predominant type of muscle fibre found in the biceps? Why?
What factor can influence the proportion of fibre types in a muscle?
How may muscle fibres change during endurance training?
When do voluntary contractions occur?
When there are strong contractions due to increased voluntary effort are there more or less motor units activated? What would their frequency be like?
What is fatigue in muscles?
What factor may increase the extent to which muscles can be activated in individuals?
What is contraction in muscles dependent on?
What happens to calcium in the muscles following contraction? Where does it go?
What is the rate of movement of calcium into the sarcoplasmic reticulum dependent on?
What happens to the calcium concentration when muscles contract?
What is DOMS?
When do giant motor unit potentials occur?
When 100% of the contractile machinery is activated what is the value for the concentration of calcium available?
True or false: there are large stores of ATP in muscles?
When none of the contractile machinery is activated what is the calcium concentration in the cell?
What is creatine phosphate used for in muscle cells?
Is there more or less CP in cells than ATP?
How is ATP produced during anaerobic respiration? What other products build up?
What happens to the rate of calcium returning to the SR if there is a 10 degree fall in temperature?
What is peripheral fatigue a result of?
Is peripheral fatigue more likely in maintained contraction or quick bursts of contraction? Why?
What is tetanic contraction?
Define a fused tetanus.
Define an unfused tetanus.
What is the function of the sarcotubular system?
What Ca2+ receptors are activated in the sarcotubular system upon arrive of an AP from tubules/sarcolemma?
Where is Ca2+ released from in the sarcotubular system?
Does Ca2+ activate troponin or tropomyosin?
What are the five major steps in cross-bridge cycling?
How does an overcontracted muscle affect the tension in the muscle?
What are transverse tubules a result of?
What is excitation contraction coupling?
What is a motor unit in muscles?
What is a motor neuron pool and where does it occur?
What is the delay between an action potential in the motor neurone and an action potential in a muscle?
Describe the process of events that occurs in neuromuscular transmission.
What happens to the acetylcholine involved in neuromuscular transmission once the action potential has occurred?
What is the enzyme that is used to synthesise acetylcholine (and CoA) from choline and acetyl CoA?
True or false: under normal conditions only 1 muscle fibre AP is triggered for each nerve AP due to the rapid breakdown of ACh.
To which subunit in the ACh nicotinic receptor does ACh bind?
In muscle cells what are the names given to the cell membrane and the cytoplasm?
What forms the sarcotubular system?
Which is the thick filament and which is the thin filament in the myofibrils?
What is the A band made up of?
What would you call the distance between two Z lines?
What are the dimensions of thin actin filaments?
What regulatory proteins cover actin/myosin binding sites on actin?
What are the three parts of thick myosin filaments?
What is the displacement of myosin heads?
What is the sliding filament theory?
When myosin heads are in cocked/normal/upright position what do they contain: ATP or ADP + Pi?
When/where are cross bridges formed?
What is the 'power stroke' in muscle contraction?
What are the stages in cross bridge cycling (starting from cross bridge attachment)?
Below what level does calcium concentration need be for contraction to end?
What are T tubules?
Describe the difference between the distance of Z lines in an uncontracted sarcomere and a fully contracted sarcomere?
During contraction which bands of the myofibrils stay constant and which bands vary?
Does the muscle cell get darker or lighter during contraction? Why?
What part of the nervous system generally supplies skeletal muscle? What neurotransmitters/receptors are used in this part of the nervous system?
What are the two types of motor neurone?
What is the clinical relevance of the two types of motor neurones?
What are hyperactive reflexes?
What happens during isometric contraction of a muscle?
Why do the neurones at neuromuscular junctions have lots of myelin?
What happens during isotonic contraction of a muscle?
What does the length-tension relationship state? What is it due to?

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes