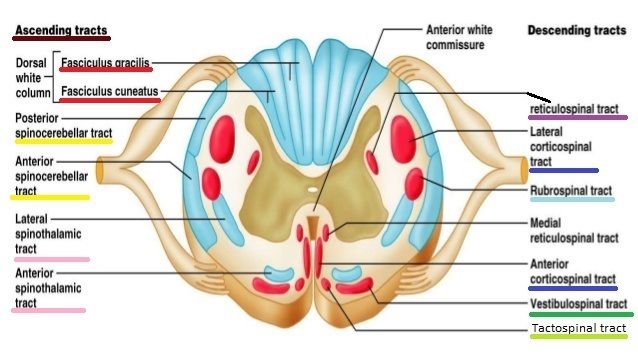
Ascending tracts
- Relay station for primary feed back (sensory)
- Main afferent tracts
- Fasciculus gracilis/cuneatus (Anterior/posterior)
- Sensory
- For trunk, neck, UE propioception, vibration, two-point discrimination, and graphesthesia
- Spinocerebellar tract (dorsal/ventral)
- Sensory
- Ipsilateral subconscious, proprioception, tension of muscles, joint sense, and posture.
- Spinothalamic tract (anterior)
- Sensory
- Light touch
- Spinothalamic (lateral)
- Sensory
- Pain and temperature
- Fasciculus gracilis/cuneatus (Anterior/posterior)
Descending tracts
- Involved with voluntary motor function, muscle tone, relfexes, and equilibrium (motor)
- Main efferent tracts
- Pyrmidal motor types
- Corticospinal tract (anterior)
- Motor
- Ipsilateral skilled movements
- Corticospinal tract (lateral)
- Motor
- Contralateral fine movements
- Damage to this may cause positive Babinski sign, loss of fine movement, and voluntary movement.
- Corticospinal tract (anterior)
- Extrapyramidal motor types
- Reticulospinal tract
- Motor
- Facilitation/inhibition of voluntary and reflex activity
- Rubrospinal tract
- Motor
- Gross posture tone
- Facilitating flexor muscles
- Inhibiting extensor muscles
- Tectospinal tract
- Motor
- Contralateral postural muscle tone
- Vestibulospinal tract
- Motor
- Ispsilateral posture adjustments
- Damage to this may cause in paralysis, hypertonicity, exaggerated deep tendon reflex.
- Reticulospinal tract
