List the basic functions of the nervous system. Explain the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system
Pinned to
170
1
0
No tags specified
|
|
Created by Sabith Iqbal
almost 9 years ago
|
|
Rate this resource by clicking on the stars below:




 (0)
(0)
Ratings (0)
| 0 | ||
| 0 | ||
| 0 | ||
| 0 | ||
| 0 |
0 comments
There are no comments, be the first and leave one below:
Close
6768732
note
2016-10-25T00:33:03Z
3/5
Peripheral Nervous System
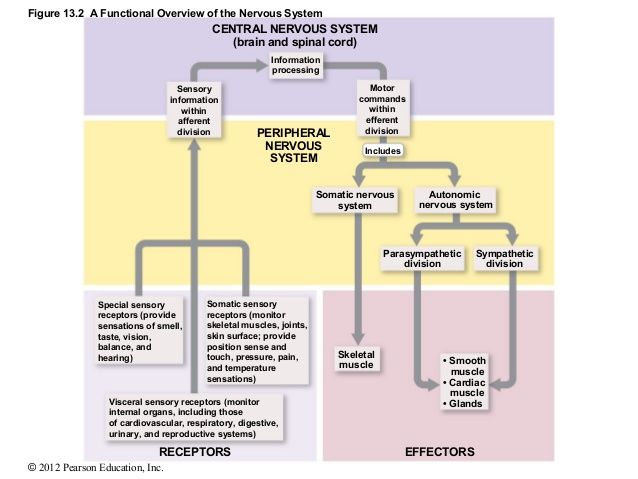
All the parts of the nervous system outside the Central Nervous System (CNS). Consists mainly of nerves (bundles of axons) which extend to and from brain and spinal cord.
Carry impulses to and from:
Subdivisions of Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):
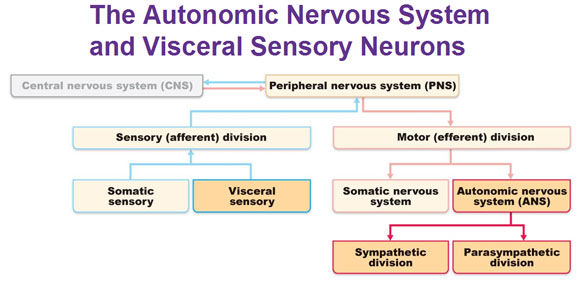
Sensory/ Afferent Division (af'er-ent = carrying toward)
Functions:
Consists of nerve fibers (axons) that convey impulses to the central nervous system (CNS) from sensory receptors throughout the body.
Keeps Central Nervous System (CNS) constantly informed of events going on inside and outside body.
Two types:
Motor/ Efferent Division (ef'er-ent = carrying away)
Functions:
Consists of nerve fibers (axons) that convey impulses from the central nervous system (CNS) to effector organs (muscles & glands).
Impulses activate muscles to contract and glands to secrete.
Brings about a motor response
Two parts:
Carry impulses to and from:
- brain - cranial nerves
- spinal cord - spinal nerves
Subdivisions of Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):
- Sensory/ Afferent division
- Motor/ Efferent division
Sensory/ Afferent Division (af'er-ent = carrying toward)
Functions:
Consists of nerve fibers (axons) that convey impulses to the central nervous system (CNS) from sensory receptors throughout the body.
Keeps Central Nervous System (CNS) constantly informed of events going on inside and outside body.
Two types:
- Somatic (soma = body) sensory fibers - convey impulses from the skin, skeletal muscles, and joints
- Visceral sensory fibers - convey impulses from visceral organs (organs within the ventral body cavity)
Motor/ Efferent Division (ef'er-ent = carrying away)
Functions:
Consists of nerve fibers (axons) that convey impulses from the central nervous system (CNS) to effector organs (muscles & glands).
Impulses activate muscles to contract and glands to secrete.
Brings about a motor response
Two parts:
- Somatic Nervous System - consists of somatic motor nerve fibers that conduct impulses from CNS to skeletal muscles. Also referred to as voluntary nervous system because it allows us to consciously control our skeletal muscles
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) (autonomic = a law unto itself) - consists of visceral motor nerve fibers which regulates smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and glands. We cannot control activities of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and glands so Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) is also called the involuntary nervous system. Has two subdivisions, sympathetic division and parasympathetic division.