16393274
The Living Cell
Description
No tags specified
Flashcards by Alice Hathaway, updated more than 1 year ago
More
Less
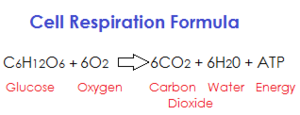
|
Created by Alice Hathaway
over 5 years ago
|
|
Resource summary
| Question | Answer |
| Archaea | Enzymes form extremophiles e.g. thermostable DNA polymerase |
| Cell Membrane | Maintain chemical integrity by separation - amphipathic bilayer. Best in liquid crystallised state. Selective permeability |
| Cell wall | Fully permeable. Cellulose in plants - most abundant polysaccharide Peptidoglycan Chitin |
| Gram Bacteria | POSITIVE -> thick pepdioglycan and membrane under. Purple NEGATIVE -> membrane, thin peptidoglycan then membrane. Pink. Bacteria won't work - cannot active peptidoglycan |
| Information Storage requirements | Molecule must be stable and accessible - rapid replication without error |
| DNA | Major and minor grooves allow access to information. Genome = total DNA in organism |
| Genes | Not all encode proteins and some may encode multiple (alternative splicing) |
| Plasmids | Readily transferred, antibiotic resistance. Horizontal gene transmission - rapid spread |
| DNA packaging | 2m in cells. Octomer form nucleosome and further folding. Chromatin packing regulates gene expression |
| Nucleus | Contains pores, regulated bu NPC above 60,000 Da. Mammals 3-4000 pores |
| Central Dogma | DNA replication -> transcription -> translation One way system |
| DNA -> protein | Transcription and translation Spontaneous 3D folding |
| Ribosomes | 2 main chain rRNA and over 50 proteins. Small and large subunit 70s -> (50s large/ 30s small) 80s -> (60s large/ 40s small) rRNA made in nucleolus Smaller subunit = protein assembly framework, large = catalyst for amino acids into polypeptide |
| ER | Makes 10% cell volume Signal peptide recognised by translator proteins to allow them to move through ER |
| Proteomics | Large scale protein analysis 80,000 proteins in human cell |
| Metabolism | Chemical reaction release energy from catabolism, or use energy in anabolism |
| Metabolomics | Study of cellular metabolites. Changes can occur from stress/ environment. Use to diagnose/ treat disease/ test drug retention times |
| Specific environments | Enabled through membranes Different pH Proteins organised in arrays |
| Peroxisome | Oxidative reactions (e.g. breakdown fatty acids). Make myelin sheath hence issue could cause neurological disease |
| Glyoxysome | In plants Convert fats to sugar via glyoxylate cycle |
| ATP | High energy final bonds due to phosphate repulsion being overcome Terminal phosphorylate other molecules to drive anabolic reactions Chemiosmosis and substrate level phosphorylation |
| ATP synthase | 100 ATP per second. Rotation action Chemiomosis |
| Mitochondria | Outer membrane smooth and permeable Inner very impermeable, but rich to proteins for energy transduction Membrane potential 160mV across inner membrane drives ATP synthesis 0.001% of nuclear DNA |
| Chloroplast | Phototransduction Thylakoid membrane of flattened vesicles forming grand. 3pH difference drives chemiosmosis Not made denovo - arise by division of different ones |
| Transport of proteins | Requires transit across membranes via transporters Fate depends on amino acid sequence - no signal remains in cytosol Others have sorting signals recognised by complementary membrane translators Sorting signal 15-60 amino acids. Removed by peptidases |
| Entrance/ exit from cell | Enter through endocytosis Leave through exocytosis |
| Vesicle Movement | flow along organised routes. Budd off from donor Polarised Golgi cistern - material enters from cis end and leaves via trans. Small vesicles transfer between cistern - each has different enzyme and environments. Chemically modified e.g. ogliosaccharide |
| Cytoskeleton | Dynamic. More refined in eukaryotes 3 filament types - microtubules, intermediate filaments, actin filaments |
| Microtubules | Set position of organelles and direct transport |
| Intermediate filaments | Mechanical strength |
| Actin filaments | Shape and movement of cell |
| Interactions and assembly | All interact with accessory proteins to control assembly and structure and regulate interactions e.g. motor proteins heir structures - non-covalent hence rapid assembly/ disassembly |
| Microtubule | 25nm, hollow cylinder. Heterodimer of alpha and beta tubular. Bind head to tail into protofilaments and assemble side to side into cylinder of 13 protofilaments. Polar - alpha minus end, beta positive. New subunits added more readily to + end Used in plants in cell shape |
| Kinesin and Dyenin | Kinesin to + end and dyeing to - end. Hydrolyse ATP and bind to microtubules and cargo. Cycle of bind and release moves 1 step at a time Kinesis 2-3um/sec, dyenin 14um/sec |
| Use motors | Able to move vesicles and mRNA to make more efficient processes ER binds to kinesin/ Golgi binds to dyenin |
| Actin filaments | 7nm 2 parallel chains of actin in helix. More rapid growth at + end High concentration in cell membrane Used by bacteria to move in cytoplasm |
| Myosin | Close relation to kinesin + end directed motors, move material along actin Regulate cell shape |
| Intermediate filaments | 10-12nm Elongated subunits Cross linked in strong arrays for mechanical stability. Keratins stabilise outer layers of skin/hair/nails Nuclear laming - meshwork outside nuclear envelope |
| Bacteria tublin | forms Z ring in bacteria and chloroplasts for cell division |
| Cilia | metachronal waves over long sheets. beat then relax. 6-10u, dyenin bridges produce sliding |
| Flagella | sperm and protists undulating wave from base to tip. 50-200um Prokaryote thinner, each attached by hook to protein discs in wall - miniature turbine |
| Ciliary and flagella | Rooted in cortex by basal bodies inconvertible to centriole in centriole doublets of microtubules in 9+2 configuration, linked by accessory proteins |
| Defects in cilliary dyenin | Kartagener's syndrome Lung infections, sperm immotile, opposite body axis |
| Generation of daughter cells | Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis-contractile ring and myosin pinches) |
| Adhesive junctions | Most fundamental in cell communication, Adhesion to each other for common extracellular material secretion. Transmembrane junction protein links - actin intermediate associated |
| Channel forming junctions | Direct passage between adjacent cells - animal gap junctions for passage of inorganic ions and small polar molecules. Formed my hexametric complexes Coordination of cell activities regulated by small molecules Permeability regulated by Ca2+ or pH |
| Plasmodesmata | Plant cell channel forming junctions Bridge cell wall with cytoplasmic channels Form as cell divides - cytokinesis incomplete to form |
| Other junctions | Occluding (tight) Signal -relaying |
Want to create your own Flashcards for free with GoConqr? Learn more.
