16398216
Microscopy
Description
No tags specified
Flashcards by Alice Hathaway, updated more than 1 year ago
More
Less
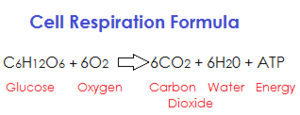
|
Created by Alice Hathaway
about 7 years ago
|
|
Resource summary
| Question | Answer |
| Light microscopy principlesM | Light focussed onto specimen by lenses in condenser Objective and eyepiece lenses focus image |
| Limits to light microscopy | only 0.2um resolution due to light wavelength Cannot see colourless (e.g. much of cell biology) |
| Staining | Increase contrast, however must be killed and preserved as cut sections so not live cells |
| Phase contest microscopy | Live cells can be seen Phase of wave changes when passes through different density Contrast created when 2 sets of waves combine |
| Scanning electron microscopy | Electron wavelength shorter so higher resolution Fixing and drying specimen then coating with thin layer of heavy metal e.g. gold Scattering of electrons creates 3d image Amount of scattering depends on angle |
| Transmission electron microscope | Cells stained with heavy metal salts to create electron dense regions Electrons pass through unstained regions and focussed to form image Vacuum prevents electron scattering by air Cells must be fixed and very thin sections as limited penetrating power Issues by artefacts |
| Fluorescent and Confocal Microscopy | Fluorescent dyes linked to antibodies to label molecules and laser and computer technology activates fluorescence and collect emitted light from single focal plane optical slice of cell viewed without out-of-focus laters interfering |
| Advantages of these | Can create 3d images Can following living cells when combined with green fluorescent protein/ tags to locate protein interaction and dynamics Use FRAP and FRET |
| X-ray crystallography | Ordered crystals scatter x-rays to give diffraction spots - patten given information of atoms via electron density Can determine protein structure Optimal conditions required |
| Cell fractionation, centrifugation, sedimentation | Open cells via osmotic shock, ultrasonic vibration or homogenisation, but leave organelles in tact Spinning separates those differing largely Sucrose density gradient allows greater separation degree |
| What happens to broken membranes? | Release into microsomes |
| Velocity sedimentation | Speed at which component separates = S value If sucrose concentrated, sub cellular components stabilise at position where density matched surroundings (equilibrium sedimentation) |
| Mass Spectrometry | Routine technique for protein identification and characterisation Proteins digested into peptides by protease Precise mass gives unique fingerprint Further fragmentation during ionisation gives amino acid sequence Mass information can identify post-translational modifications (e.g. glycoprotein) |
Want to create your own Flashcards for free with GoConqr? Learn more.
